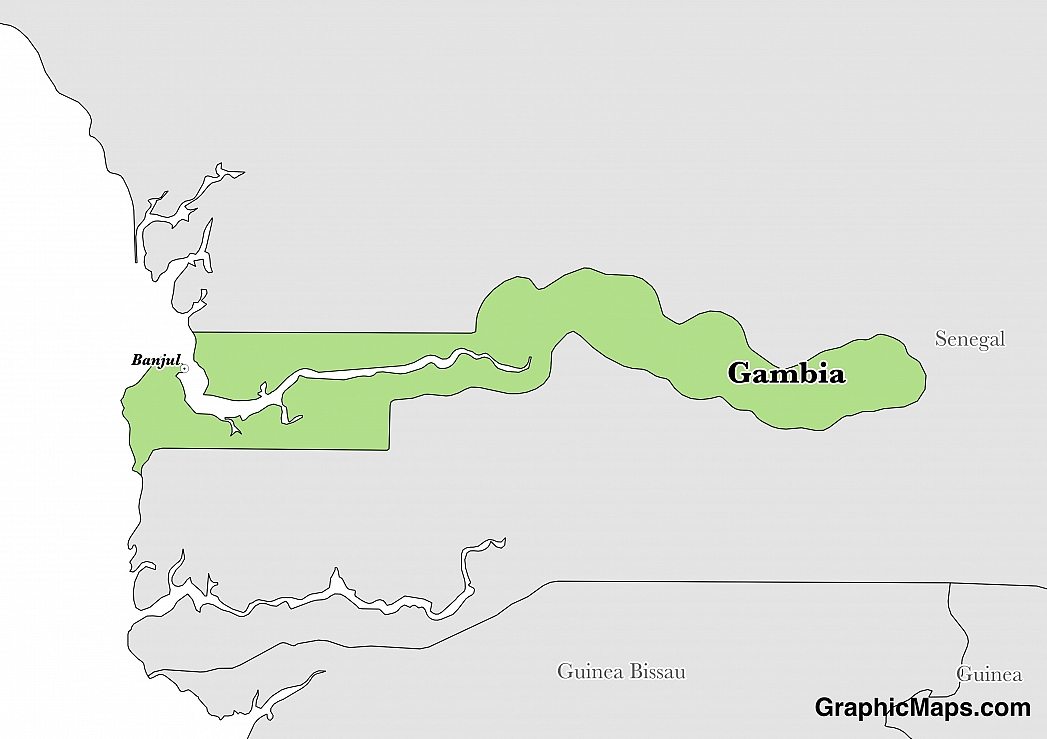
Where is Gambia?
Located in Western Africa, Gambia has a 749.00 km border with Senegal. It has a 80.00 km coastline. The border is sometimes the site of cross-border raids, arms smuggling, and other illegal activities.
Banjul is Gambia’s capital city. The city’s location is near the Gambia River which is the source of the country’s name. Banjul had a city population of 31,301 in 2013 and an urban population of 413,397. The high urban population a result of the combination of the number of people in Banjul and those within the Kanifing Municipal Council. The city of Banjul became a capital in 1816. Places to visit in Banjul include the Ma Cumba Jallow Street, Bijilo Forest Park, Brufut Beach, and Sanyang Village and Beach. The city’s climate is tropical with dry and wet seasons.
Read more on Gambia's CapitalGambia is an African country covering 11,300.00 km2 of which 10.44% is water and 10,120.00 km2 is land. This makes it the 36th smallest country in the world and slightly less than twice the size of Delaware. Its geographic coordinates are 13 28 N, 16 34 W and Banjul is the capital city.
The country is named for the Gambia River which flows through it.
Its ISO code is GM.
Geography
Gambia has a mean elevation of 34 m above sea level.
It has a tropical climate with a rainy season from June to November and a dry season from November to May. Its terrain is characterized by low hills.
Population
Gambia has a population of 2,009,648 making it the 146th largest in the world.
English is the official language. The major ethnic groups include Mandinka/Jahanka, Fulani/Tukulur/Lorobo, and Wolof. The country has a Muslim religious majority.
Gambia’s official language is English, making it one of the few anglophone West African countries. However, it is not uncommon to notice the infiltration of French into Gambia. Some of Gambia’s population comfortably speaks French. Besides English and French, the other languages spoken among Gambians include Mandingo, Fula, Wolof, and Jola among others. Mandinka is the major local dialect spoken by about 38% of Gambians.
Read more on Gambia's LanguagesThe dialing code for the country is 220.
Government
Gambia is an independent country. It gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1965. Its constitution was last ratified in 1997.
Similar to many West African nations, Gambia is a republic with the president as its leader. The president is the head of state as well as the head of government. Further, the government constitutes the judiciary, executive, and legislative arms. Gambia’s National Assembly’s location is in Banjul. The president of Gambia lives in Gambia’s State House which is also located in Banjul. In Gambia, elections occur after every five years. Out of the 58 members of parliament, 53 of them are voted in by the people of Gambia during the elections. Also, the people also vote for the president of their choice.
Read more on Gambia's GovernmentEconomy
The currency of Gambia is the Dalasi (GMD).
Its major export partners are China, Bulgaria, and Turkey. Its main exports are peanut products, fish, and cotton. Its major import partners are China, Brazil, and Senegal. Its major imports include foodstuffs, manufactures, fuel, machinery, and transport equipment.
Flag
The flag of Gambia is used both as a symbol of national unity and as a civil ensign. The flag's name is the “Standard of the President.” It consists of the colors of white, green, blue, and red. It consists of three rectangles designed horizontally across the flag. The red color symbolizes the proximity of Gambia to the equator. It also shows that it is part of the savanna region. Green symbolizes the country’s dependence on agriculture as a way of life and white stands for peace. Furthermore, the blue color represents the waters found in Gambia such as the Gambia River. The flag of Gambia was adopted in 1965. Its designer was Louis Thomasi.
Read more on Gambia's FlagThis page was last modified on January 17th, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
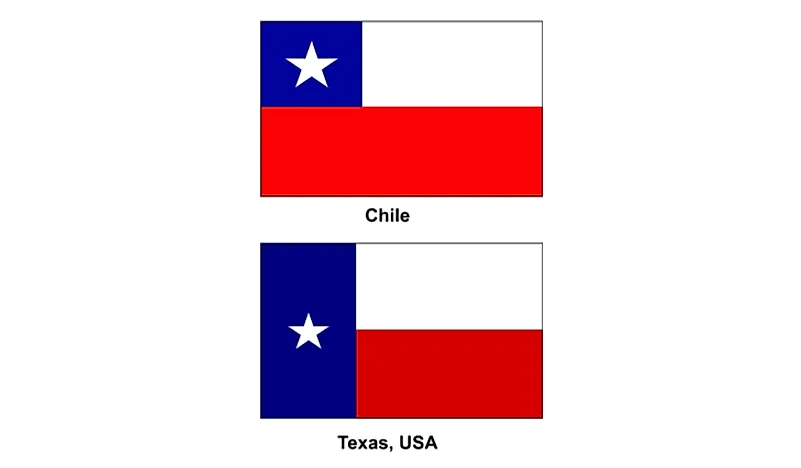
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20