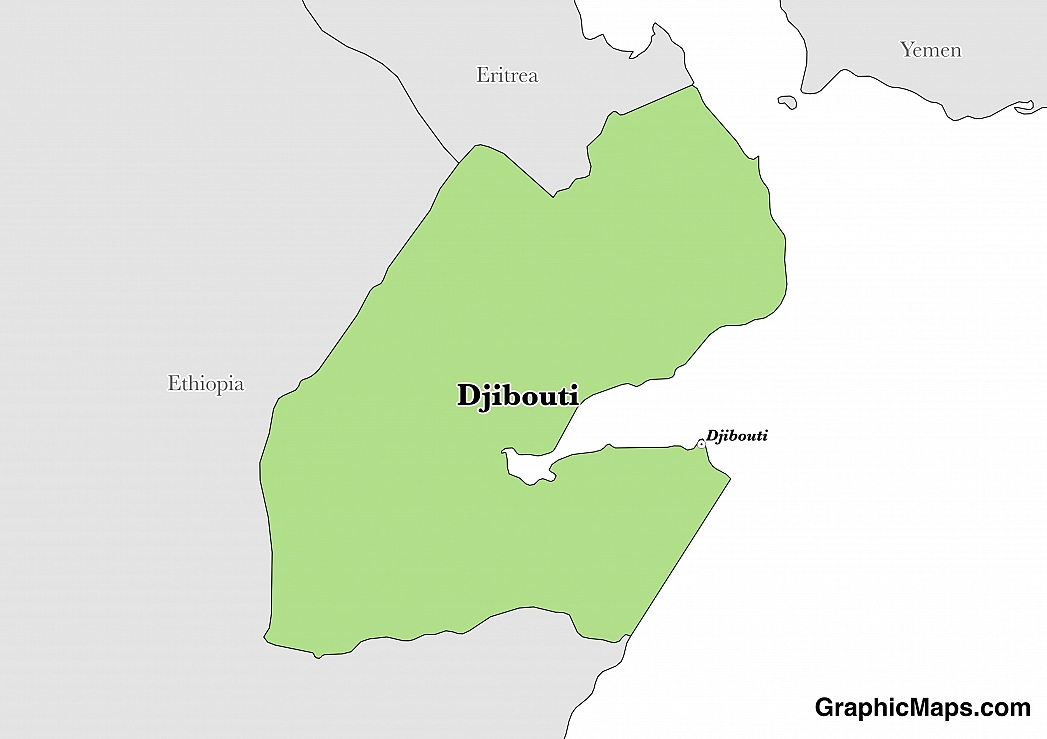
Where is Djibouti?
Located in Eastern Africa, Djibouti has a 528.00 km border with Eritrea (125 km), Ethiopia (342 km) and Somalia (61 km). It has a 314.00 km coastline. Djibouti maintains economic ties and border accords with Solaliland leadership, while maintaining some political ties to various factions in Somalia.
The capital city of Djibouti is Djibouti City, located in the eastern part of the country and situated in the Gulf of Aden in the Horn of Africa. The area was established as a trading port in 1888 by French colonialists and is well-known for its 19th-century colonial architecture. Djibouti City was formerly a part of French-Somaliland until the country gained independence in 1977 and is strategically positioned in one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world. The urban area is divided into 21 districts and is the cultural, financial, and educational center of Djibouti. The climate of Djibouti City is classified as an arid environment with hot, humid, and dry summer months. This period of the year sees average highs reach 42 degrees Celsius (108 degrees Fahrenheit). The population of the city is estimated at just over 530,000 with many citizens being from Afar or Somali descent. 94% of inhabitants are considered Muslim and the remaining populace are considered Christian or Catholic. The city serves as a major transportation hub for the region with an international airport, and extensive road and rail network accompanying the port.
Read more on Djibouti's CapitalDjibouti is an African country covering 23,200.00 km2 of which 0.09% is water and 23,180.00 km2 is land. This makes it the 49th smallest country in the world and slightly smaller than New Jersey. Its geographic coordinates are 11 30 N, 43 00 E and Djibouti is the capital city.
The country gets its name from its capital city of Djibouti.
Its ISO code is DJ.
Geography
Djibouti has a mean elevation of 430 m above sea level.
It has an arid climate which is very dry. Its terrain consists of a coastal plain and plateau separated by central mountains.
Population
Djibouti has a population of 846,687 making it the 161st largest in the world.
French and Arabic are official languages. The majority ethnic groups are Somali, Afar, and other. The majority of the population identifies as Muslim.
The official languages of Djibouti are Arabic (an Afro-Asiatic language) and French (Indo-European). French has been inherited from the nation's colonial past and Arabic has cultural, religious, and societal roots. Djibouti is considered a bilingual nation with many important signs and announcements in both Arabic and French as well as regional dialects where applicable. Although they are not considered official languages, Somali and Afar are the most widely spoken with approximately 88% of the country speaking either of these dialects. Somali has over 520,000 speakers in Djibouti and Afar has just over 300,000. Just 17,000 native Djibouti citizens speak French as a first language and 59,000 speak Arabic as their native tongue. Minority languages in Djibouti include the Amharic, Oromo, and Ta'izzi-Adeni Arabic dialects, an example of the languages that migrants have brought to the country. There are also small communities of Greek and Hindi speakers. The main foreign language of Djibouti is English and many schools now teach English as a mandatory subject. Although many in the country understand English, Arabic and French phrases will also be useful in Djibouti.
Read more on Djibouti's LanguagesThe dialing code for the country is 253.
Government
Djibouti is an independent country. It became independent from France in 1977. Its constitution was last ratified in 1992.
The political system of Djibouti can be classified as a presidential representative democracy in a republic nation. Executive power is held by the Government and President and Djibouti and legislative power is vested in the Government and National Assembly. The President of Djibouti is considered both the head of state and head of government. In 1977, the people of Djibouti voted for independence from France but the national constitution was not implemented until 1992. The country is also an active member of the Arab League and the United Nations. The President of Djibouti is elected every six years and the parliament is elected every five. The country is divided into five regions, with 11 additional district subdivisions, and one city for administrative and electoral purposes.
Read more on Djibouti's GovernmentEconomy
Factoring in Purchasing Power Parity, Djibouti's GDP is $3,345,000,000.00 (USD) with $3,400.00 (USD) per capita. This makes it the 182nd largest economy and its citizens the 178th richest in the world. The currency of Djibouti is the Franc (DJF).
Its major export partner is Somalia. Its main exports are reexports, hides and skins, coffee, and scrap metal. Its major import partners are China, Saudi Arabia, and Indonesia. Its major imports include foods, beverages, transport equipment, and chemicals.
Flag
The flag of Djibouti consists of two horizontal stripes of light blue (top) and green (bottom) with a white triangular wedge on the mast side that intersects both stripes. The white triangle contains a red, five-pointed star in the centre. This flag became the official national banner of the country on 27 July 1977 after the nation declared independence from France. Mahamoud Harbi, a politician, designed the national flag that is used today. Harbi was the Vice President of French Somaliland (the area that contained Djibouti), as well as a prominent independence advocate. He was exiled to Cairo in 1960 and died in mysterious circumstances while promoting independence for the area in 1961. The light blue is a representation of the clear skies and Gulf of Aden as well as the Issa Somalis ethnic group. The green is a symbol of the earth and agricultural traditions, in addition, the green is also associated with the Afar peoples. The white triangle is symbolic of peace and the red star is a symbol of the people who fought, and died, for independence in Djibouti. This flag is known as Calanka Jabuuti in Somali and Drapeau de Djibouti in French.
Read more on Djibouti's FlagThis page was last modified on January 17th, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
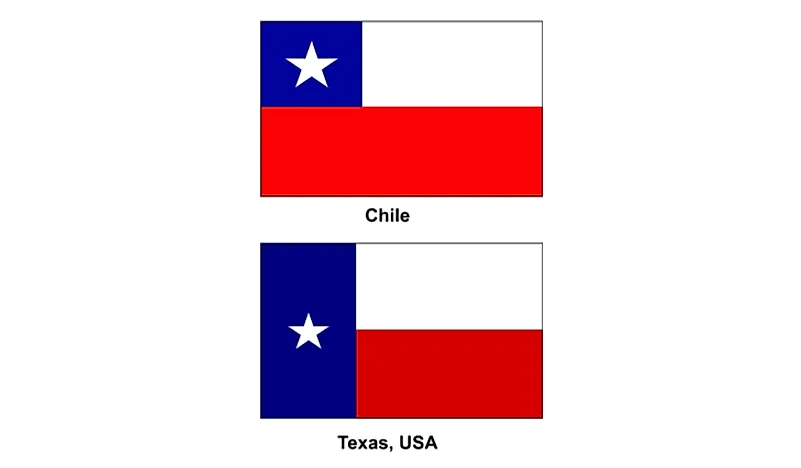
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20