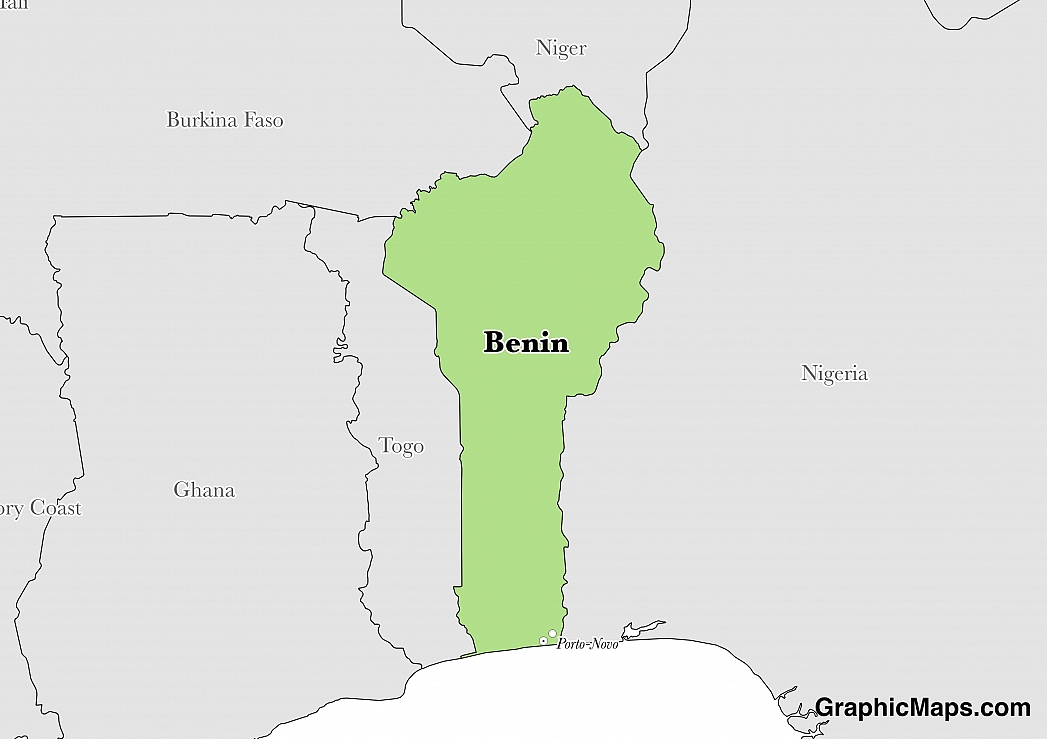
Where is Benin?
Located in Western Africa, Benin has a 2,123.00 km border with Burkina Faso (386 km), Niger (277 km), Nigeria (809 km) and Togo (651 km). It has a 121.00 km coastline. Talks continue between Benin and Togo on funding the Adjrala hydroelectric dam on the Mona River.
The capital city of Benin is Porto-Novo which is located in the southern part of the country near the Gulf of Guinea. The name Porto-Novo is Portuguese for "new port" and the city became the capital in 1900 during the French colonial period. Porto-Novo is also known as Hogbonu and Ajashe. The city was used as a port for the slave trade during the 1800s and the region produces cotton and palm oil. Oil was discovered off the coast of Porto-Novo in 1990 and has become an important source of income for the country. The climate of Porto-Novo is consistently warm throughout the year and is considered a tropical environment. The average temperature at any time of the year in Porto-Novo is 27.4 degrees Celsius (81 degrees Fahrenheit) and the warmest months are February, March, and April, each with an average temperature of 28 degrees Celsius (82 degrees Fahrenheit). The population of Porto-Novo was last measured in 2009 at 267,191 citizens, many of whom are from the Ogu or Yoruba ethnicities. There are also many citizens in Porto-Novo who hail from the neighbouring countries of Nigeria, Burkina Faso, and Togo
Read more on Benin's CapitalBenin is an African country covering 112,622.00 km2 of which 1.78% is water and 110,622.00 km2 is land. This makes it the 100th largest country in the world and slightly smaller than Pennsylvania. Its geographic coordinates are 9 30 N, 2 15 E and Porto-Novo is the capital city.
The country is named for the Bight of Benin, the body of water upon which the country lies.
Its ISO code is BJ.
Geography
Benin has a mean elevation of 273 m above sea level.
It has a tropical climate which is hot and muggy in the south and semiarid in the north. Its terrain is mostly flat with some hills and low mountains.
Population
Benin has a population of 10,741,458 making it the 85th largest in the world.
French is the official language; Fon and Yoruba are also widely spoken. The major ethnic groups are Fon, Adja, and Yoruba. The country is mostly made up of Muslims, Catholics, and Protestants.
The official language of Benin is French. However, there are a total of 50 indigenous languages that are also considered national dialects. American Sign Language is also an official means of communication in Benin. Of the native Beninese languages, the most prevalent in the south are Fon and Yoruba. In the northern part of the country, there are half a dozen common languages including Bariba and Fulfulde. French is used in the commercial, educational, governmental, and media sectors in Benin. Approximately 35% of the population of Benin speak French as a native language which equates to roughly 4 million people. The language is considered prestigious in the country and many who seek employment in the cities of Benin learn French in order to improve their chances of gaining a job. All print media in Benin is in French and the language connects the citizens of the country through one common dialect. A large proportion of the population will learn multiple languages and are known as polyglots. Minority languages in the country are vast but the most spoken is Fon which belongs to the Volta-Niger branch of the Niger-Congo language family. Almost one-quarter of the population of Benin speak Fon with 17% speaking it as their first language. Fon is spoken mainly in the Atlantique, Collines, Littoral, and Zou regions of the country.
Read more on Benin's LanguagesThe dialing code for the country is 229.
Government
Benin is an independent country. It gained independence from France in 1960. Its constitution was last ratified in 1990.
The political system of Benin takes place in a presidential representative democratic republic. The President of Benin is the head of government as well as the head of state. The current system is outlined in the 1990 Constitution of Benin before the transition to democracy in 1991. This constitution reformed the political and economic system of the country after the collapse of the Soviet Union which had influenced and funded the Marxist government from 1975-1990. Executive power in Benin is held and exercised by the government and legislative power is vested in the government and the national legislature. The legislature of Benin is known as the National Assembly and is located in the capital city of Porto-Novo which is in the southern part of the nation. This parliament was first founded in 1959 and prior to this time, citizens of Benin took part in heavily controlled elections to vote a representative to the French National Assembly. The National Assembly has pledged to combat corruption, illiteracy, and lack of transparency in many sectors in Benin. Elections in Benin for the presidency usually take place every six years but the next election is scheduled for 2012, 5 years after the last election in March of 2016. All 83 seats in the National Assembly are elected by the people of Benin every five years.
Read more on Benin's GovernmentEconomy
Factoring in Purchasing Power Parity, Benin's GDP is $24,310,000,000.00 (USD) with $2,200.00 (USD) per capita. This makes it the 140th largest economy and its citizens the 194th richest in the world. The currency of Benin is the Franc (XOF).
Its major export partners are India, Gabon, and China. Its main exports are cotton, cashews, and shea butter. Its major import partners are China, the United States, and India. Its major imports include foodstuffs, capital goods, and petroleum products.
Flag
The flag of Benin consists of a horizontal red and yellow band on the right-hand side and a vertical green band on the mast side. This flag was originally adopted on 16 November 1959 to replace the flag of France when the country was known as the Republic of Dahomey. After a new regime has taken power in 1975 the country was known as the People's Republic of Benin and used a different flag until 1990 when this version was re-adopted. As Benin was previously a French colony, the flag of France was flown from 1892-1959 across the region. One year before full independence in 1960, the current flag was officially adopted. From 1975 until 1990 a Marxist government took power and renamed the country the People's Republic of Benin. The flag that was used during this time consisted of an army green field with a red, five-pointed star in the top left-hand corner. The original design is meant to reflect solidarity with other African nations who had gained independence around the same time. The colours are also important cultural, religious, and regional symbols in Benin which is why this design was selected. The same colours are featured on the flag of Ethiopia which is the oldest independent nation in Africa.
Read more on Benin's FlagThis page was last modified on January 17th, 2018
More on Graphicmaps

Published on 2019-11-06
What is a Trade Embargo?

Published on 2019-11-04
Which Two Countries Used to Have the Same Flag?

Published on 2019-09-16
What Is the Only Two-Sided State Flag?
Published on 2019-09-16
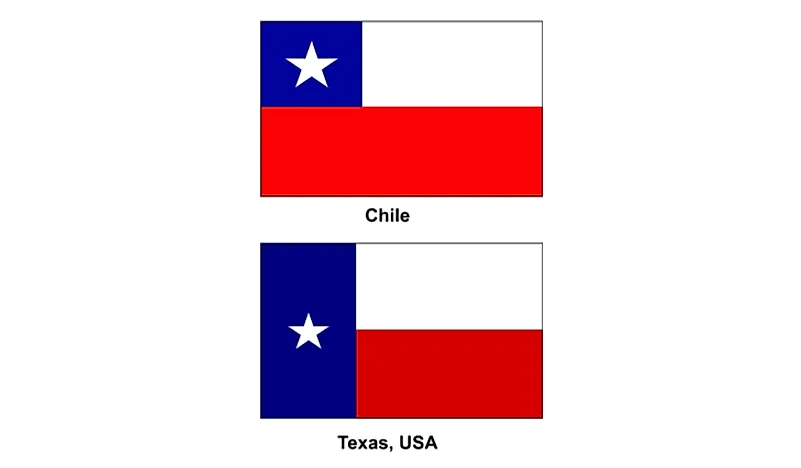
Which Country Flag Looks Like the Texas Flag?

Published on 2019-08-29
Flags That Resemble the US Flag
Published on 2019-08-20